Web Protection
Web Protection provides an extra layer of security to protect you from suspicious websites while you are surfing the Internet.
What does Web Protection actually do?

Web Protection keeps watch as you browse the web and warns you when you try to access a malicious website. By blocking your connection to dangerous hosts, Web Protection prevents data from being exchanged and minimizes the risk of malware infecting your machine.
A host can be defined as a website domain such as www.google.com or an IP address that might contain data for several domains. Hackers often use single physical servers with unique IP addresses that dozens of different domains point to. Emsisoft’s Web Protection is able to detect new malware domains reliably and halts all exchange of data – unless you as the user explicitly grant access.
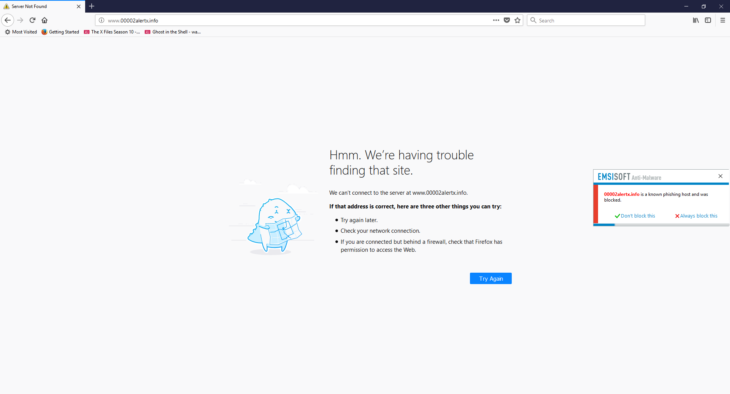
Emsisoft Web Protection Notification
One of the key benefits of Web Protection is that it intercepts connections at the Windows system level. This ensures that Web Protection not only works with browsers but almost all programs, and doesn’t require compatibility updates whenever a new version of your browser is released.
How does Emsisoft’s Web Protection recognize suspicious hosts?
In addition to a massive collection of conventional malware signatures, Emsisoft Anti-Malware also has a huge database of known malicious and otherwise dangerous hosts. The data is gathered from publicly available lists, intel from specialized companies that Emsisoft has partnered with, and verified user submissions. To keep the database up to date and provide maximum security against the latest malicious websites, new threats are continually added and the list is updated every 15 minutes.
There are different categories of suspicious hosts:
- Malicious hosts: Suspected to spread malicious software such as bots, ransomware, trojans, adware, rootkits or viruses, and phishing hosts that attempt to steal your passwords via fake clones of well-known websites.
- Unwanted hosts: Engaged in distribution of potentially unwanted programs.
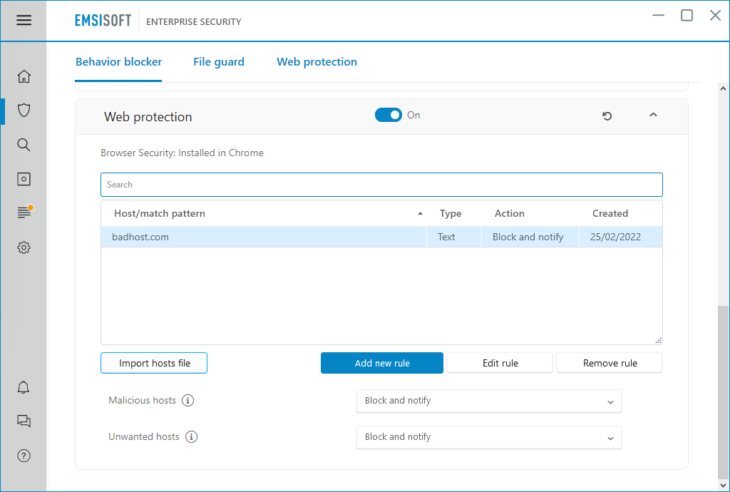
How to configure Web Protection
Emsisoft Anti-Malware’s default settings offer maximum security and are simple to use. However, you can change the settings at any time to meet your individual needs.
How to add a new host rule
You can add your own custom host rules that overwrite the built-in blocklist by clicking ‘Add new rule’. There you can specify if you want to use a simple text based matching on the host name/IP, or a more complex Regular Expression based matching pattern. See: What is a RegEx?
How to change custom host rules
Double-click a rule or select a rule and click ‘Edit rule’ to open the edit window.
Host rules feature the following actions:
- Don’t block: Allows access to the host without asking.
- Alert: Alerts about access, and lets you decide whether to block or to allow it.
- Block and notify: Blocks the connection automatically and displays a notification pop-up window to let you know about it.
- Block silently: Blocks the connection, but does not show any notification.
We recommend using the default setting “Block and notify” so that you will know immediately when a connection has been blocked. This may keep you from wondering why a certain website has not loaded.
How to import a third party hosts file
The hosts file is part of Windows and is located in c:\windows\system32\drivers\. It is used for overriding DNS settings by redirecting certain domains to certain IP addresses in a targeted manner. Various hosts file lists are available to download online and this has been a popular method used by people to build their own form of “web protection” with tools that come with Windows. Malicious domains are then redirected to the local IP 127.0.0.1 or the invalid endpoint 0.0.0.0, which both neutralize them.
There are some disadvantages to this approach, though. You never know when a connection has been redirected, and a large hosts file can slow down your system’s performance. There are also no automatic updates, so you have to keep your hosts file list up-to-date yourself.
If you wish to use third-party hosts file lists, we recommend you import them directly into Emsisoft Anti-Malware instead, by using the “Import hosts file” option which allows you to import individual entries as well as larger lists in one go. Unlike using a custom Windows host file, importing a third-party list into Emsisoft Anti-Malware’s Web Protection, will not slow down your system. Use of third-party lists is purely optional – most entries are already on the built-in list that is updated every 15 minutes.
How is Web Protection different to Browser Security?
The difference is in the technical approach. Web Protection works like a local firewall that blocks connections to known bad domains/IPs. That works system-wide with all programs, not just browsers.
Browser Security on the other hand is a browser extension that runs inside the (typically sandboxed) browser process and therefore can look at the full URL path, not just the domain/IP. That means it can do more sophisticated filtering using RegEx matching to alert specific areas of a website only.
Imagine a malware file is stored somewhere on drive.google.com. Web Protection would only be able to block Google Drive as a whole, which is impractical as it would also block access of millions of users to their data too. But the browser extension can match with a single path where the malware file is located.
See Browser Security for details.